Scientists have carried out a study that could have found a possible cause behind the rising cases of a certain cancer.
The conclusion was reached after reviewing over 3,000 studies on the potential cause, and it’s something that lifestyle and genetics can’t really explain.
Colon cancer cases among young people are rapidly on the rise, as a study’s findings showed that it kills 17,000 people per year in the UK.
While it has been previously suggested by the American Cancer Society that it’s all down to the Western diet, it turns out it could be something else entirely.

The researchers analysed thousands of results before coming to a conclusion (Getty Stock Photo)
What could be a major cause of colon cancer?
Californian researchers posted their findings and review in the ACS Publications Environmental Science & Technology this month, and found one potential cause of the deadly disease.
They found that tiny toxins from microplastics may have a suggested link to lung and colon cancer, in addition to other lung diseases and even infertility.
It adds to the baffling scientific discovery that lung cancers not caused by tobacco are currently rising, as the health world continues to learn more about cancer and its many causes.
What are microplastics?
Microplastics are small pieces of plastic (less than 5mm in diameter) that are released by consumer goods – think clothes, toys, packaging, food containers or even tyres.
Not only do they contaminate the air, our food and our water, but they can now be found inside of our bodies, potentially causing inflammation.
If the immune system were to react to it, a number of medical issues may rise such as tissue damage and heart inflammation.
Scientists believe there could be a possible link between microplastics and colon cancer, among other health issues, though with plastic production expected to continue increasing, researchers from the University of California are calling it a ‘big concern.’

Microplastics can be incredibly harmful to your health (Getty Stock Photo)
How can microplastics cause health issues?
The review, which looked at 3,000 studies across animals and humans, found that exposure to microplastics can cause long-term problems in the respiratory, digestive and reproductive systems.
The team explained: “We concluded that exposure to microplastics is ‘suspected’ to adversely impact the colon and small intestine in humans.”
Basically, the studies showed there was a possible link between microplastics and negative changes in the digestive system, as the particles can disrupt the mucus layer which protects us.
What do the researchers think?
They continued: “Across the outcomes, we identified that exposure to microplastics is ‘suspected’ to be a digestive hazard to humans, including a suspected link to colon cancer, using the key characteristics of carcinogens approach.”
Some studies found a link between microplastics and a low birth rate, though the review stated: “We concluded that exposure to microplastics is ‘suspected’ to adversely impact sperm quality and testicular health in humans.”
A link between poor lung function and microplastics present in the organ were also found, labelled as a ‘hazard’ to the respiratory system.
Colon cancer is a rising issue among younger adults (Getty Stock Photo)
Researchers added that these small particles are ‘widespread’, and can be found virtually anywhere, including the Antarctic, Arctic and ocean trenches.
This means they can easily enter the human body and have even been found in breastmilk, the liver and human placenta.
Senior author Tracey J.Woodruff, professor of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences at UCSF, stated: “These microplastics are basically particulate matter air pollution, and we know this type of air pollution is harmful.”

A doctor has explained the common symptoms of a cancer that has rising cases in young people.
While Cancer Research UK points out in its statistics that Hodgkin lymphoma is not among the 20 most common cancers, incidence rates are projected to rise by 13 percent between 2023 – 2025 and 2038 – 2040.
It can develop at any age but it mostly affects people between 20 and 40 years of age and those over 75, with a 2022 study noting that its increase has been especially noticed in the younger population – though it further states that the reason is still unknown.
The cancer develops in the lymphatic system which is part of your immune system and is a network of vessels and glands spread throughout your body – with one sign sometimes appearing when you drink alcohol.
Dr Ahmed is a GP based in the UK and shared a video to TikTok urging people to not ignore ‘if you have any symptoms’.
.jpg)
It’s commonly spotted in the neck, armpits and groin. (Getty Stock)
“So, in Hodgkin lymphoma, a certain type of cell called B lymphocyte grow in number abnormally,” he explains. “They cluster together in certain parts of your body, most often your armpits, neck and groin.”
And so, Dr A says the ‘most common symptom’ is therefore a lymph node ‘that’s inflamed and enlarged that won’t go away again’.
He points out that you want to keep an eye out for these lumps particularly in your neck, armpits or groin.
“If you’ve got one of these or a lymph node that’s not going away after four to six weeks, you must get it checked out,” the doctor adds.
He also includes other symptoms such as ‘a persistent fever, persistent cough or breathlessness, a high temperature and weight loss’.
While diagnosis ‘can be quite quick’ the NHS explain the only way to do so is by carrying out a biopsy.

Hodgkin lymphoma typically spreads quickly. (Getty Stock)
This is a minor surgical procedure where they will remove a sample of affected lymph node tissue to be studied in a lab.
Dr A advises that the cause of Hodgkin lymphoma isn’t exactly known, but there are risk factors including: “If you’ve got a weakened immune system, if you’ve previously had glandular fever, have a family history.”
The NHS also adds that your risk of developing it is increased if you take immunosuppressant medicine.
“Treatment can involve radiotherapy and chemotherapy and prognosis is fantastic,” Ahmed says.
And while it is a ‘relatively aggressive cancer’ and can spread through the body quickly, it is one of the most easily treated types of cancer.
Overall, around eight out of 10 patients live at least five years and most of them will be cured.
The doctor adds this ‘is why it’s important you get diagnosed early and see a doctor if you have any risk factors or symptoms’.
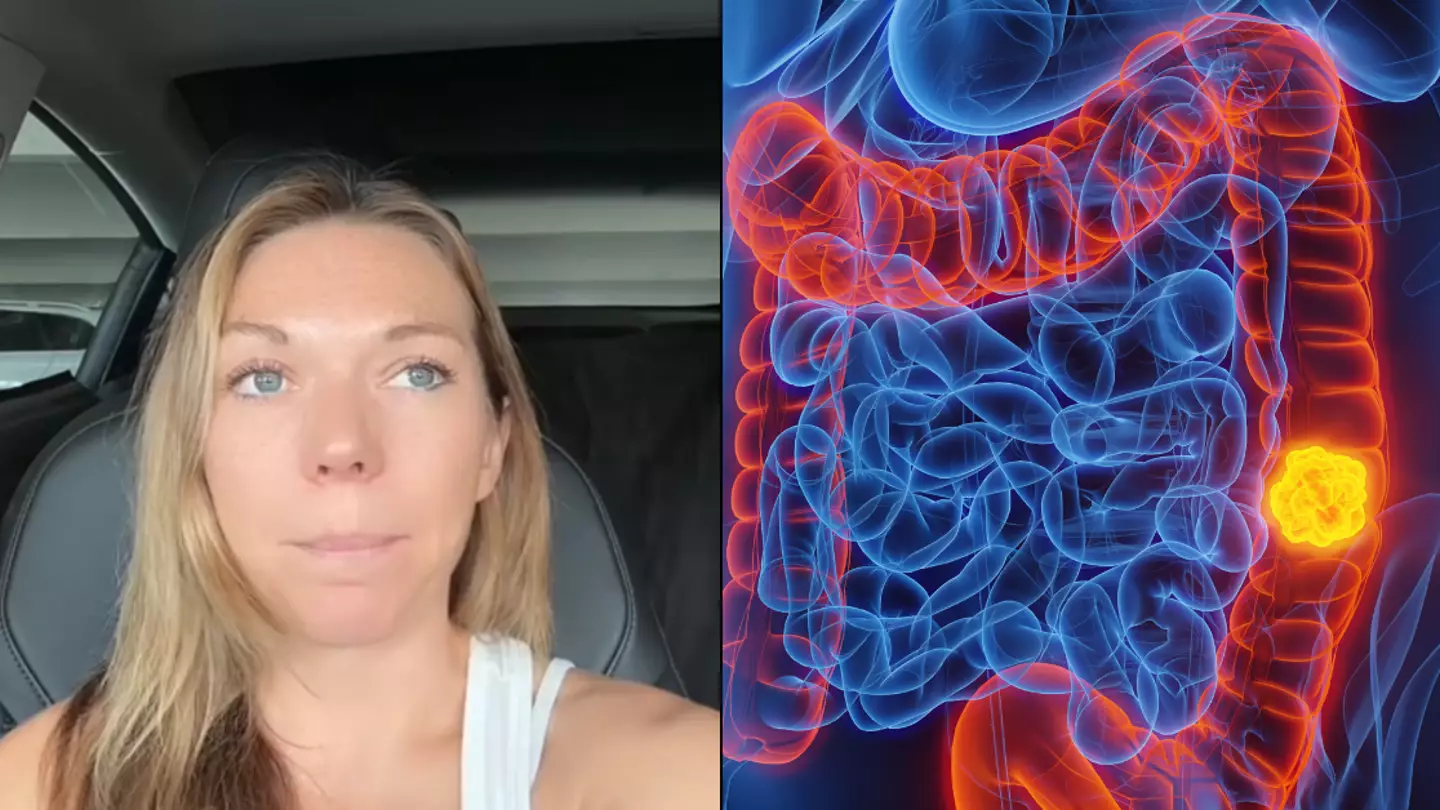
A woman diagnosed with a hard-to-detect cancer shared the key symptoms she experienced as cases soar among young people.
Earlier this year, figures found that bowel cancer (often referred to as colon or rectal cancer) was rising in those under 50 years old.
This type of the disease is when it’s found anywhere in the large bowel which includes the colon and rectum.
While it is one of the most common types of cancer in the UK, the symptoms can often be dismissed by patients as something else – but the NHS encourage early bowel cancer screenings as it may mean it’s easier to treat.
And only in her 30s, TikToker Bri Mahon found she had stage 3 colorectal cancer.
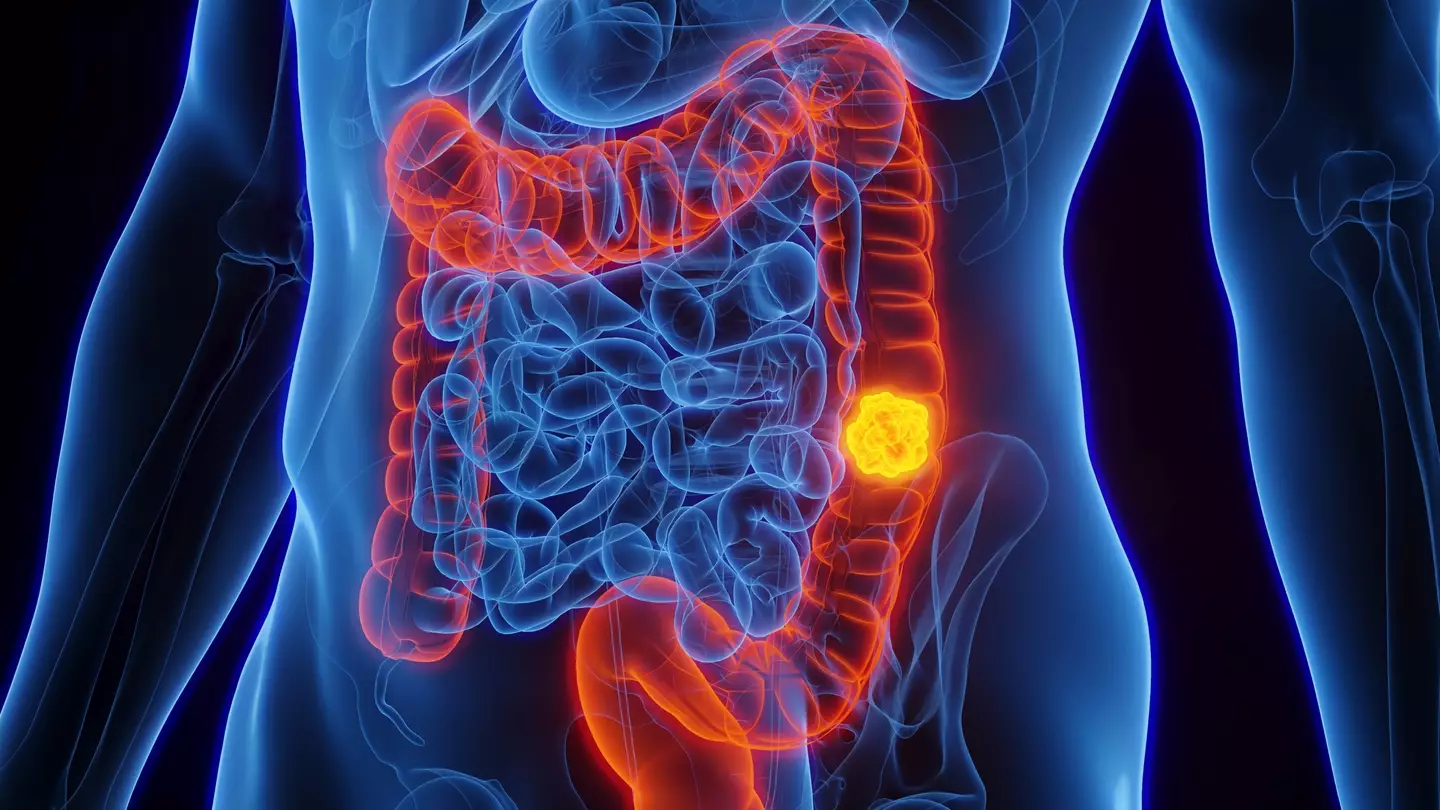
Bowel cancer is said to be one of the hardest cancer to detect (Getty Images)
She shared a video to the social media platform to share all of her symptoms that led to her ‘getting checked out and getting a colonoscopy’.
Bri says she had ‘just gut issues in general’ for some time like bloating, adding that the signs ‘would point more towards Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)’.
But when she cut out the likes of gluten and dairy and took various allergy and blood tests, ‘nothing concerning came up’.
Feeling as though her stomach was ‘irritated and bloated a lot’, she then noticed a ‘change in her anxiety and fatigue’.
Around two years ago, she had to ‘step back’ from the work she was doing and thinks it’s because her body ‘was really, really, really tired’.
.jpg)
The woman brushed off her symptoms. (Getty Stock)
Then after giving birth to her twins premature, she noticed blood in her stool shortly after, passing it off as ‘haemorrhoids from pregnancy’.
“My IBS symptoms were flaring up, and I just kind of thought that was it,” Bri added.
With her babies in the NICU, she was stressed out and tired anyway so justified any fatigue and stomach problems as being down to that.
“But it’s when I found and started to see more regular blood in my stool. I got pretty concerned as kind of like red blood,” she explained.
“And then I really got concerned when the blood turned a lot darker, and my urgency to go to the bathroom was kind of like out of control, and I would either be insanely constipated or I’d be going to the bathroom and just dark blood would be coming out.”
Bri says this only happened for a few months and it led to her calling her doctor.
At first, they thought it could be an autoimmune disease, but following a colonoscopy and biopsies, they found it was stage three cancer.
To the list of bowel cancer symptoms, the NHS include blood in your poo, bleeding from your bottom and feeling very tired for no reason.
If your poo is black or dark red or you have bloody diarrhoea, you should ask for an urgent GP appointment or get help from NHS 111.
If you’re bleeding non-stop from your bottom or there’s a lot of blood, for example, the toilet water turns red or you see large blood clots, then go to A&E or call 999.
Doctors have issued a warning to young people about three new factors that seem to be connected to a certain type of cancer that has seen cases skyrocket.
New research has pinpointed these factors which could be to blame for the global colon cancer epidemic among young people, as diagnoses continue to rise.
Colorectal cancers are increasing in young Americans, with diagnoses expected to rise by 90 percent by 2030 in those in their 20s and 30s.
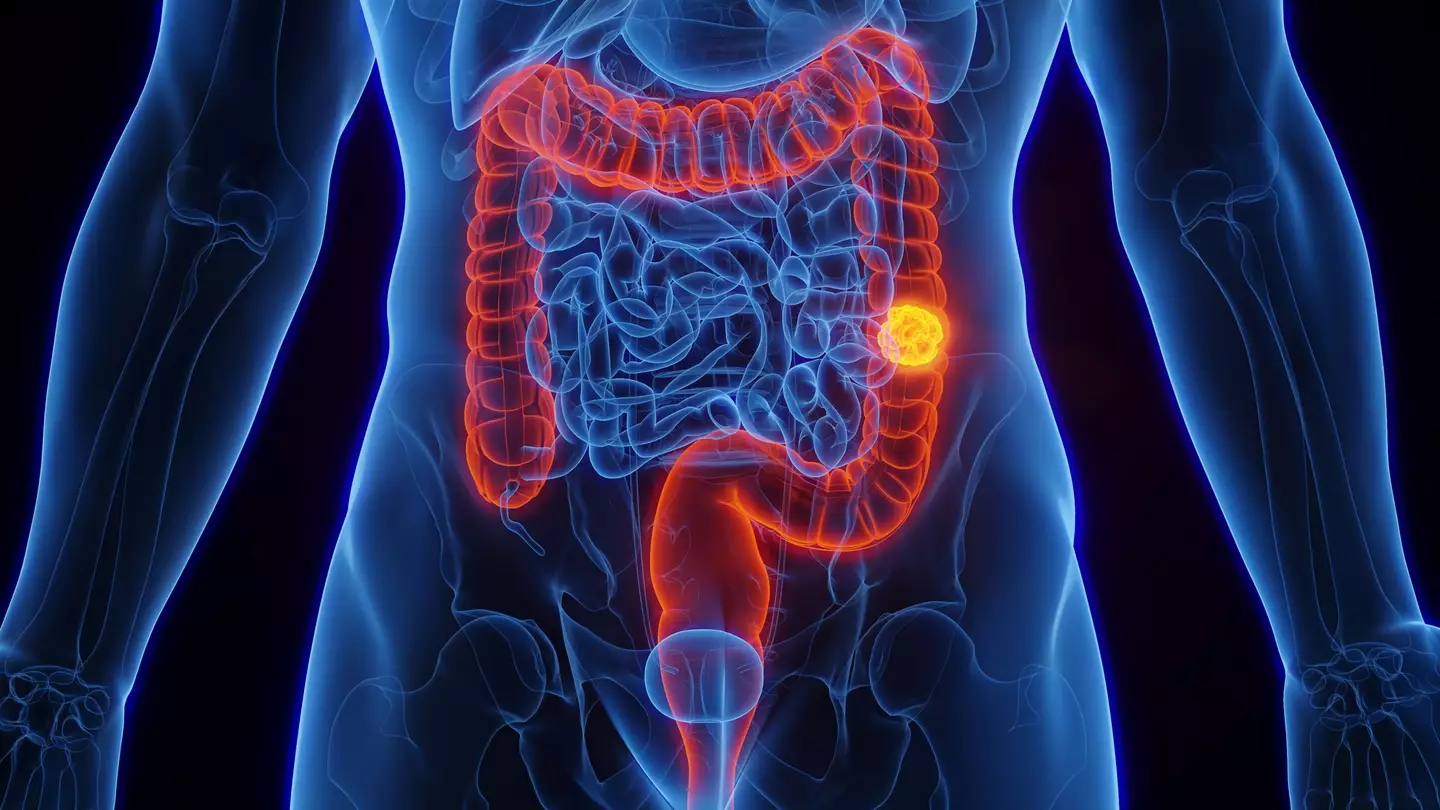
Colorectal cancers are on the rise amongst young people (Getty Stock Image)
While bad diets and being overweight have been blamed, this doesn’t explain the surge in cases among those who are seemingly fit and healthy.
Now, a new review of over 160 studies has suggested that pesticides in food, toxins in drinking water and air pollution could potentially be the cause.
Yes, chemicals in food, air and water could potentially be to blame for the surge in cases – especially in America.
Research showed that this ‘complex interplay’ of factors changes bacteria in the gut, which consequently leads to chronic inflammation. This then leads to healthy cells being killed off and cancerous cells to grow.
It was also suggested that this increase in early-onset colorectal cancer, known as EOCRC, has long been i the making due to an increased exposure to pollutants, which can be traced back to 1950.

Chemicals in food, air and water could potentially be to blame for the surge in cases, according to recent research (Getty Stock Image)
In the journal Heliyon, researchers wrote: “Consequently, there is a pressing need for enhanced environmental policies aimed at minimizing exposure to pollutants, safeguarding public health, and mitigating the burden of EOCRC.”
The team, from Sultan Qaboos University in Oman, also said that gastrointestinal health is dependent on gut microbiome – a network of bacteria which regulates the digestive and immune systems.
A lifetime of exposure to things such as foods, antibiotics and chemicals can alter this system, leaving it in an ‘unstable state’ with dangerous bacteria overpowering healthy bacteria.
Researchers also noted the consumption of water that has been contaminated with heavy metals like lead and arsenic – the EPA has estimated that 9 million lead pipes are still in use across the US.

Environmental factors could be causing cancer in fit and healthy people (Getty Stock Image)
In a bid to gain an insight into the rising cases, the researchers also looked as environmental exposures in people born after 1950.
They highlighted a group of microscopic particles which are so small the nose and lungs cannot filter them out, known as PM2.5 or fine particulate matter.
These particles are emitted directly into the air from fossil fuels burned from factories, as well as gasoline-powered stoves and cars, and can easily travel to the bloodstream, leading to inflammation.
Researchers claimed PM2.5 triggers inflammation in the colon, which has been shown to cause the development of cancer cells and impact the immune system’s ability to fight them off.
There is a form of cancer that is rising rapidly among those under 30 for a particular reason, experts have said.
The health condition is rising in younger people, as well as bowel, breast and lung cancer, with Cancer Research UK revealing an 84 percent increase in the condition in Brits aged 24 to 49 since the 1990s.
It isn’t exclusive to the age group, however, as it affects the whole population, but it looks like this age group has seen the largest increase.
And health experts have revealed that one factor in particular is to blame for this as it is a gastrointestinal issue.
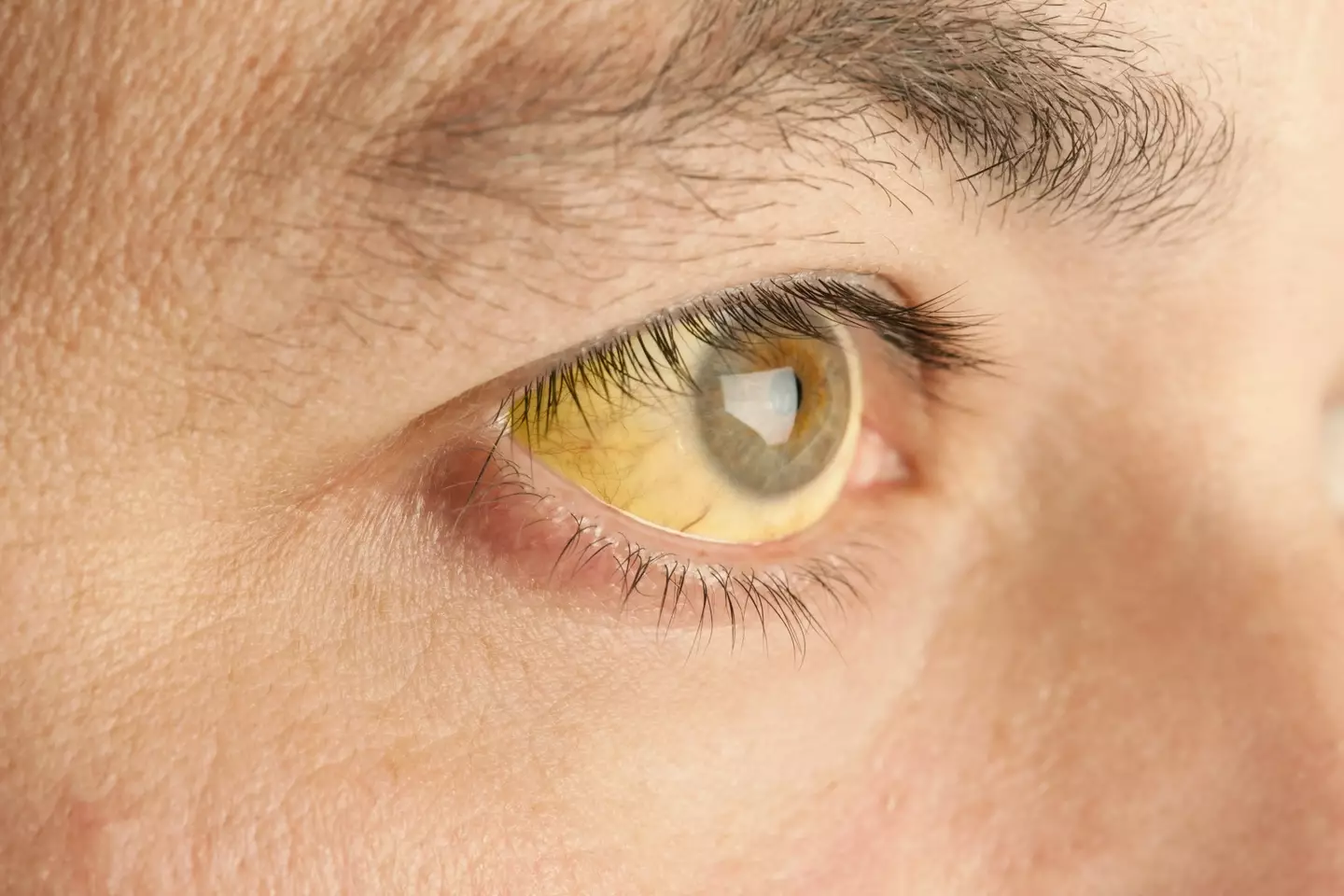
There’s a leading cause to the increase in cancer diagnoses among young people (Getty Stock Photo)
It’s all to do with subtle changes to bacteria in your gut, which is affected by the factor in question.
Cancer risk increases as you get older, with it becoming much higher once you pass 50, according to Cancer Research UK, but it looks like there is a concerning increase in early onset cancers, with more people being diagnosed under 50.
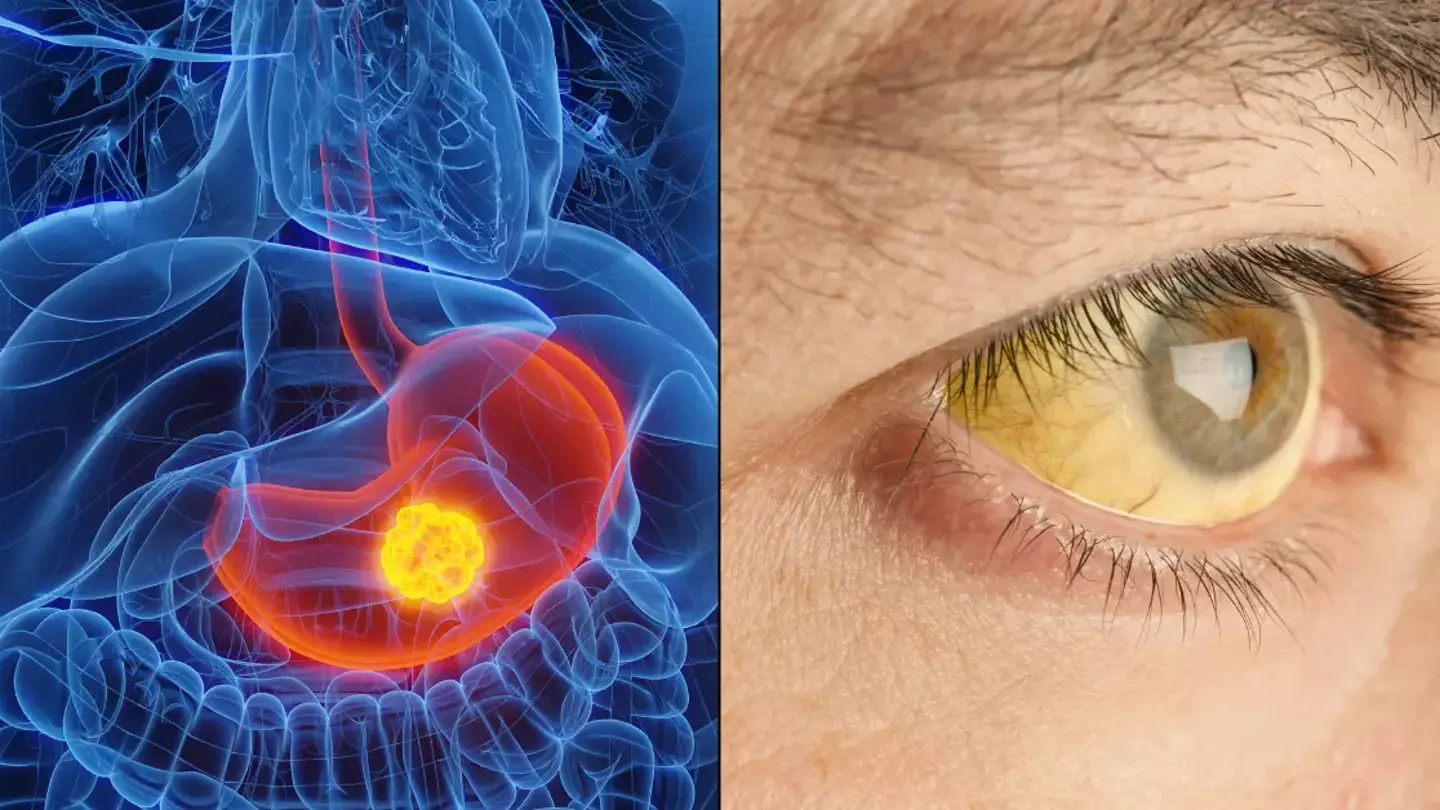
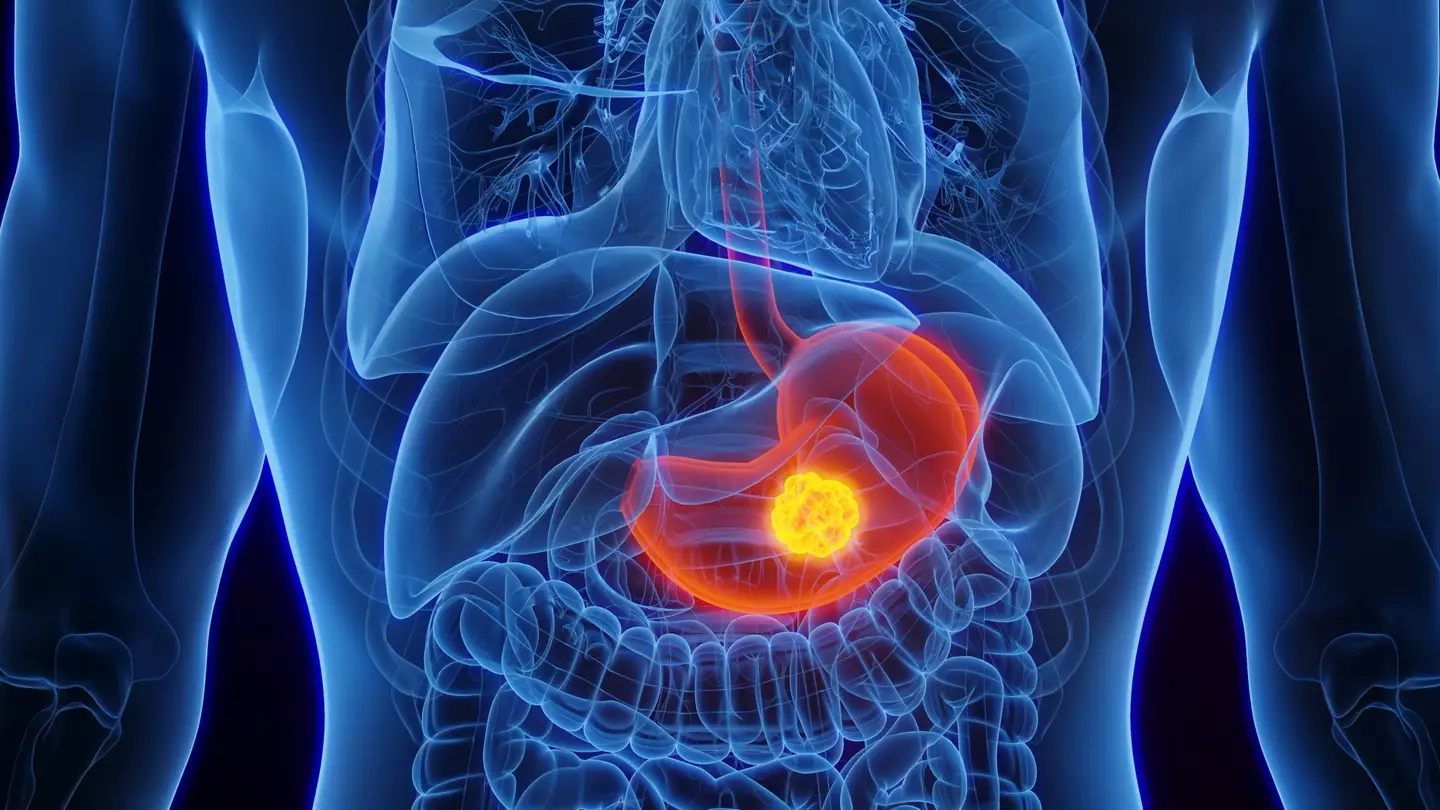
The type of cancer that is increasing specifically for young people for is gallbladder cancer and though little known, it’s worth noting what the main causes behind it might be.
Where is the gallbladder?
The gallbladder is an organ the size of an apple located near the liver, known for storing bile, which is a substance that helps our body break down fats that we ingest, according to the National Health Institute (NIH).
Though gallbladder cancer is rare, with 1,000 cases in the UK annually, it’s on the rise among younger people, as more than twice as many young adults get the disease than 30-or-so years ago, Cancer Research UK says.
How many people are getting gallbladder cancer?
There are still only 35 cases among those aged 25 to 49 each year, though it is worrying that those in their 20s are becoming more prone to contracting the disease.
Professor Karol Sikora, an oncologist with 40 years’ experience, spoke to MailOnline and said that it’s all down to lifestyle as the increase began in the 90s.
The gallbladder is located by your liver (Getty Stock Photo)
What’s the cause behind the increase?
Professor Sikora, a former chief of the World Health Organization’s cancer programme, said that the age of patients have continued to get ‘lower and lower’.
He revealed the factor behind the increase in gallbladder cancer in young people – a modern diet.
The ultra-processed foods that are available to us are ruining our guts, as he explained that it’s also due to alcohol, pollution and junk food, which effects our microbiome in our gallbladder.
He explained: “It’s just impossible to measure…it’s a complex series of things that can affect it.”
The professor explained that it was interesting to see the trend in the generation that aim to drink less and eat healthier, with the oncologist adding that eating fruit and vegetables while exercising regularly can help to avoid getting cancer.
What are the symptoms of gallbladder cancer?
Some symptoms can include jaundice, which is when the skin and eyes turn yellow, itchy skin, and obvious changes in the colour of your poo or urine.
Data shows that only a sixth of gallbladder cancer patients live 10 years following their diagnosis.